In the learning applications world, the need of integrating the application with other platforms/tools/portals is rapidly growing. To provide a standard platform for the integration of the applications, IMS has enabled the LTI compliance.
Let us first understand the basic use and benefits of LTI.
Introduction:
IMS Global highlights, LTI (Learning Tools Interoperability) helps in establishing a standard process for integrating the rich learning applications with platforms like LMS or other educational portals. In LTI these learning applications are called Tools that are delivered by Tool Providers and the LMS platforms/portals are called Tool Consumers.
Benefits:
LTI enables plug and play into any LMS that is IMS certified. LTI provides the following benefits:
- Helps in integration of a variety of educational applications, learning tools and content into the LMS
- Enables immediate use by faculty or students, returns the outcomes data and analytics across a wide variety of learning tools, applications, and content to LMS.
- A single sign-on online environment for all users
- Reduces the number of custom integrations required for product developers because every application interfaces in the same way.
Key Concepts and Elements
LTI provides a way of connecting two systems together: a “Tool Consumer” which “consumes” the tool, and a “Tool Provider” which “provides” the Tool to be used in the Tool Consumer. Below is the image that explains the key elements and communication flow in simple way.
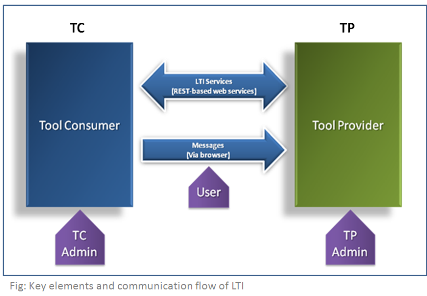
Tool Consumer
These are the learning applications in which the links to external tools are to be integrated. Typically a Tool Consumer would be an LMS.
Tool Provider
Tool Provider is the system providing access to one or more Tools. Tool Provider may include a hosted Assessment system or a variety of learning portals.
Connections:
The connection between Tool Consumer and Tool Provider takes place using LTI services or messages.
User:
Represents a person logged into a Tool Consumer. The authentication process can be driven through other systems like an LDAP server. The user will have a unique identifier.
Many learning management systems, including the most widely used in education across the world, already support LTI and this trend is also supported by many application and content vendors
Stay tuned for the next blog which will explain the connection concept of LTI. Service based and Message based are two types of connections, which help in connecting the Tools Consumer and Tools Provider.
Do share your experiences with integration of learning tools and platforms, in the comments below, and don’t forget to subscribe to the blog to get notified on our next post.






