This is a new world for searches. More and more techniques are evolving to index, manage and present the tremendous amount of data available on the net, and make it fit for users’ need. Both old and new search players are trying to shape searches and refine results. More than ever before, relevancy and context are key to “organizing the world’s information” today.
Google has introduced many new initiatives to advance relevancy in its search results. Let’s take a look at few of the most critical ones of these:
1. Latent Semantic Indexing: Google’s effective use of Synonyms to determine if a page should qualify in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) of a particular search is the basis of this. With the help of synonyms, a search about “song words” or “song writer” will also include hits with the word “lyrics” or “lyricist” in the content. Google is going one step ahead, where it will not only look at the key words for relevancy, but also scan the entire content and look for keywords as well as synonyms. If the entire content satisfies the requirement, it will be judged as relevant. This is called Latent Semantic Indexing.The purpose behind this is to index searches closer to the way a human reader would rank the page. In natural indexing, actual information rather than repetition of words would be a factor in how well the page ranks. The use of related words (synonyms) would signify that the subject is thoroughly covered.
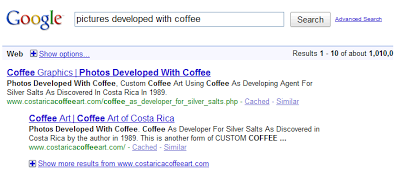
As shown in the above example from the Google blog, the search for “pictures developed with coffee” will have all the search results with synonyms for pictures, and all the synonyms along with the search terms will be displayed in bold.
2. Semantic Searches based on profiles, reviews and events: For over a year the concept of Semantic Searches is doing the rounds in full force on the search scene. RDFa and microformat have been around for quite some time, but now they have caught prime attention spot as the new wave of search.
Last year, Google announced its support for Semantic Searches with Rich Snippet. As an initial step, Google did this for two formats, people and reviews, with LinkedIn and Yelp as partners. They followed it up with semantic support for Video searches as well as events.
The concept behind this is quite simple. There are people associated with documents, pictures, companies, addresses – almost everything. Similarly, there are events associated again with a place, an address, a company, a play etc.
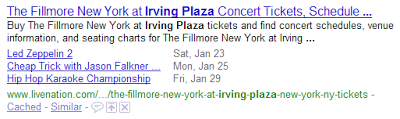
So now with the help of Rich Snippets, it is possible to tag profiles, events as well as reviews for a particular search string. An example outlined again in the Google blog shows three links to three events on Jan 23rd, Jan 25th and Jan 29th when a user searches for Irving Plaza on Google (see image below). Needless to say, this provides a fast and convenient way for a user to determine if Live Nation has any events lined up that he or she might be interested in.
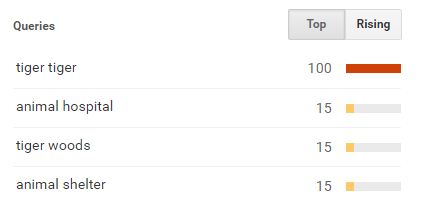
- Google Insight for Searches and Google Trends: While Google Trends show us the current search trends, Google Insight takes it one step ahead. It shows us the applicable (frequently used) keywords as well as the rising searches within a topic, so that we can make out what is the related ‘hot’ search topic. For example, if we search for “Tigers + animal”, in addition to the search trend information of these and the synonyms, Google Insight also shows us the top and the rising searches related to these words.
- There are other new initiatives from Google in beta stage, like Real Time searches, Comparison Advertisements, as well as new domains in Semantic Searches, but we will leave them to another post.
Of course, relevancy in search results has been a determining factor of the success of a search engine for decades. Google is a key player in the search world, and will definitely be an important contributor in defining the semantic web. With all the above as well as other semantic analysis techniques like context servers and usage of explicit user actions when indexing content, the search scenario for 2010 and beyond looks very interesting… And Google seems to be taking small but sure steps towards the intelligent web of tomorrow.






